In this article we will will discuss about:- 1. Meaning of Power Thresher 2. Types of Power Thresher 3. Components 4. Installation 5. Maintenance and Storage 6. Trouble Shooting.
Meaning of Power Thresher:
It is a machine operated by a prime mover such as electric motor, engine, and tractor or power tiller used for threshing.
A power thresher performs several functions such as:
1. To feed the harvest to the threshing cylinder.
2. To thresh the grain out of the head.
3. To separate the grain from the straw.
4. To clean the grain.
5. To put the grain in a bag.
6. To make bhusa (chaff), suitable for animal feeding.
Removal of seeds from the grain heads is done by rotating cylinders, whose threshing action depends primarily upon impact. When a slow moving material comes in contact with the high speed cylinder, the heads or pods are shattered and grains are freed from straw. Further threshing is done when the material passes through the restricted clearance space between the thresher cylinder and the concave portion of the unit.
Types of Power Thresher:
There are following types of thresher:
1. Hammer mill type
2. Rasp bar cylinder type
3. Spike-tooth cylinder type
4. Syndicator type
5. Drummy type thresher
1. Hammer Mill Type:
It is a thresher with threshing unit consisting of hammers or beaters with a closed cylinder casing and concave. It is equipped with a set of oscillating sieves and an aspiratory blower for separation and cleaning of grains.
2. Rasp-Bar Cylinder Type:
In this thresher, the thresher unit consists of bars with serrations having an open concave.
3. Spike Tooth Cylinder Type:
It is a thresher, the threshing unit of which consists of drum having rows of spikes with a closed cylinder casing and concave and equipped with a set of sieves and aspiratory blower.
4. Syndicator Type:
It is a thresher, the threshing unit of which consists of a corrugated flywheel with serrated chopping knives and a closed cylinder casing and concave. This is also known as chaff-cutter type thresher.
5. Drummy Type Thresher:
It is a hammer mill type thresher without separation and cleaning system. Usually a centrifugal blower is provided for partial separation and cleaning of grain.
On the basis of feeding system, the power thresher can be of four types:
i. Chute Feed Thresher:
A thresher in which the feeding of the crop is done through a chute.
ii. Conveyer Feed Thresher:
A thresher in which the feeding of crop is done through a conveyer.
iii. Feed Roller Feed Thresher:
A thresher in which the feeding is done with the feed rollers equipped with chute or an endless conveyer.
iv. Hopper Feed Thresher:
A thresher in which feeding of the crop is done through the hopper. It is also known as bulk feed thresher.
On the basis of crop, thresher may be of following types:
a. Wheat Thresher:
This equipment is used for threshing of wheat crop with or without bhusa making provision.
b. Paddy Thresher:
This equipment is used for threshing paddy crop.
c. Groundnut Thresher:
This equipment is used for threshing of groundnut.
d. Millet Thresher:
This equipment is used for threshing of millet crop.
e. Soya Bean Thresher:
This equipment is used for threshing of soya bean crop.
f. Multi Crop Thresher:
This equipment is used for more than one crop with or without minor adjustment.
This thresher has either spike tooth cylinder or rasp bar cylinder depending upon the manufacturer. It has cleaning and bagging attachments. This thresher can be used for crops like paddy, wheat, sorghum, soya bean, gram, millets etc. It can be operated by 5-20 hp power depending upon the models. Its capacity may be 300-2500 kg/hr.
Components of Power Thresher:
The main components are:
1. Concave
2. Cylinder or drum and
3. Cleaning unit
1. Concave:
It is a concave shaped metal grating, partly surrounding the cylinder against which the cylinder rubs the grain from the plant or ear heads and through which the grains fall on the sieve.
2. Cylinder or Drum:
It is a balanced rotating assembly, comprising rasp, beater bar or spikes on its periphery and their support for threshing the crop.
There are five types of threshing cylinders commonly used in the country:
(a) Peg Tooth Cylinder:
The teeth on the concave and cylinder are so arranged that the cylinder teeth pass midway between the staggered teeth on the concave. The concave assembly is pivoted at the rear portion of the machine. The clearance space between the cylinder and the concave is adjusted according to the requirement. As the stalks pass through the clearance space, the grains get separated from the head due to impact action between the teeth.
(b) Loop Type:
The cylinder is studded with a number of wire loops throughout its outer periphery. This is mostly used on paddy threshers.
(c) Angle Bar Cylinder:
Cylinder is equipped with angle iron bars, helically fitted on the cylinders. The bars have rubber pads on their faces. The concave unit is fitted with a rubber faced shelling plate and steel jacketed rubber bars. The clearance between the cylinder and concave unit at the entrance is from 13 mm to 19 mm and reduces to about 6 to 9 mm only.
(d) Hammer Mill Type:
The beaters are in the shape of hammer mill. The beaters are attached with the beater arm at the tip. Beater arms are rigidly fixed to a hub which is mounted on main shaft.
(e) Rasp Bar Cylinder:
The cylinder has corrugated bars round it. Threshing is accomplished between corrugated cylinder bars and stationary bars of the concave portion. The rotating cylinder takes the grains out from the head as it is drawn over, the bars on the concave unit. Usually 6 to 8 bars are spirally fixed on the cylinder.
3. Cleaning Unit:
The function of the cleaning unit is to separate and clean the threshed grain. The cleaning unit mainly consists of two or more oscillating sieves, a fan and an air sucking duct known as aspirator. Usually two ducts are there, one primary duct and the other secondary duct. The function of the primary duct is to remove major portion of straw, dust and other foreign matter. The secondary duct is used for final cleaning of the grains.
Thresher provided with aspirator unit is usually called aspirator type of thresher. Those threshers which are not fitted with aspirator unit have got only one blower, which blows air in horizontal direction. This type of thresher is commonly called drummy thresher.
Aspirator – It is a component of the cleaning unit used for cleaning grain by drawing air through the grain mass.
Blower – It is a device to produce air blast.
Winnower – It is a machine with one or two sieves and fan using air. Drummy thresher stream across falling grain.
Winnowing Fan – It is a machine used for creating air blast mainly for the purpose of winnowing of grains.
Seed Damage – Seed damage may occur due to cylinder concave clearance being too small. In some cases the damage is due to the impact blow which is directly related to the cylinder peripheral speed. The speed damage may or may not be visible. The internal damage may be known only by germination test.
Cylinder Adjustment – Cylinder concave clearance may be adjusted by raising or lowering the cylinder and the concave unit. Clearance should be as great as can be used with satisfactory threshing. Cylinder speeds may be changed by changing sheaves and sprockets.
Installation of Power Thresher:
1. The prime mover of thresher should be located such that blown straw does not fall on the thresher.
2. The prime mover should be kept at a safe distance from the feeding mechanism.
3. The prime mover should be suitably levelled.
4. Straw outlet should be kept in the direction of wind.
5. The power thresher should be firmly grounded for stability.
6. Proper alignment of thresher should be done.
7. Direction of rotation of belt should be properly maintained.
8. The tension of the driving belt should be maintained.
9. Guards and safety devices should be maintained. Proper feeding should be done for safety of operators.
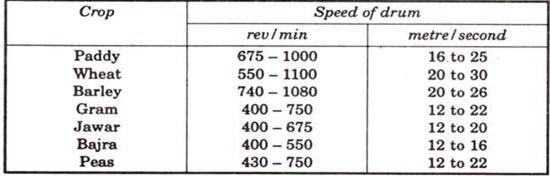
Recommended speed of threshing drum:
Diameter of thresher pulley (Dt) is given by:
Dt = Dp x Np / Nt
Where,
Dt = diameter of the thresher pulley (mm)
Dp = diameter of the prime mover pulley (mm)
Np = speed of the prime mover pulley (rev/min)
Nt = speed of thresher pulley (rev/min)
Maintenance and Storage of Power Thresher:
Preventive Maintenance of Power Thresher:
1. Belts to be checked
2. Bolts and screws to be checked
3. Foreign matter (if any) in the crop should be removed
4. Damaged and bent parts to be checked and repaired.
5. Sieves to be checked and cleaned if openings are clogged.
6. Point to be cleaned and greased.
Storage of Thresher in Off-Season:
1. Run the thresher idle for some time after the work is over.
2. Disconnect the power source and remove all the grains and straw.
3. Remove all belts, clean and store them in a safe place.
4. Wash, clean and dry the thresher completely.
5. Repaint the thresher where necessary or apply a coat of grease or used engine oil.
6. Lubricating points such as grease cups and bearings should be cleaned with kerosene oil or diesel oil and should be lubricated with fresh oil or grease.
7. Entrance of virmins should be prohibited by closing the passage.
8. The thresher should be stored in dry shed.
9. Jack the thresher frame horizontally on wooden blocks or bricks in case of pneumatic tyres.
Trouble Shooting in Power Thresher:
Some of the reasons and remedies are:
Trouble – 1- Threshing Drum is Blocked:
1. Reason – Over feeding. Remedy – Avoid over feeding
2. Reason – Belt loose. Remedy – Check all the belt
3. Reason -Drum speed too low. Remedy – Increase the speed
4. Reason – Moist crop. Remedy – Dry the crop
5. Reason – Crop infested with weeds. Remedy- Remove the weeds
6. Reason – Less concave clearance. Remedy – Adjust the proper clearance
Trouble – 2 – Broken Grains Coming Out of Thresher:
1. Reason – High speed of drum. Remedy – Decrease the drum speed
2. Reason – Less concave clearance. Remedy – Adjust the proper clearance
Trouble – 3 – Grains Blows with Straw:
1. Reason – High speed of fan. Remedy – Decrease the fan speed
2. Reason – Sieve holes blocked. Remedy – Clean the sieve holes
Trouble- 4 – Straw is Coming with Grain:
1. Reason – Low fan speed. Remedy – Adjust the proper fan speed
2. Reason – Improper size of sieves. Remedy – Use proper size of sieves
3. Reason – Too much feeding and uneven feeding. Remedy – Proper feeding should be done
4. Reason – Blocked concave. Remedy – Clean the concave
5. Reason – Low shaking speed. Remedy – Adjust the proper shaking speed
Trouble – 5 – Grain is Coming with Tailing:
1. Reason – Upper sieve blocked. Remedy – Clean upper sieve
2. Reason – Improper sieve slope and size. Remedy – Adjust proper sieve slope and use proper size of sieve
3. Reason – High shaking speed. Remedy – Decrease shaking speed
Trouble – 6 – Too Many Unthreshed Heads:
1. Reason – Low cylinder speed. Remedy – Increase cylinder speed
2. Reason – High concave clearance. Remedy – Decrease concave clearance
Trouble – 7 – Vibration in Thresher:
1. Reason – Improper installation. Remedy – Install the thresher properly
2. Reason – Bearings are loose. Remedy – Tighten the bearing
3. Reason – Worn-out components. Remedy – Repair or replace the components